Understand Nodes
Last Updated:What's in this article?
What are Nodes?
A Node is the building block of a flow. Any of the following Nodes can be used in a flow.
- Start Node
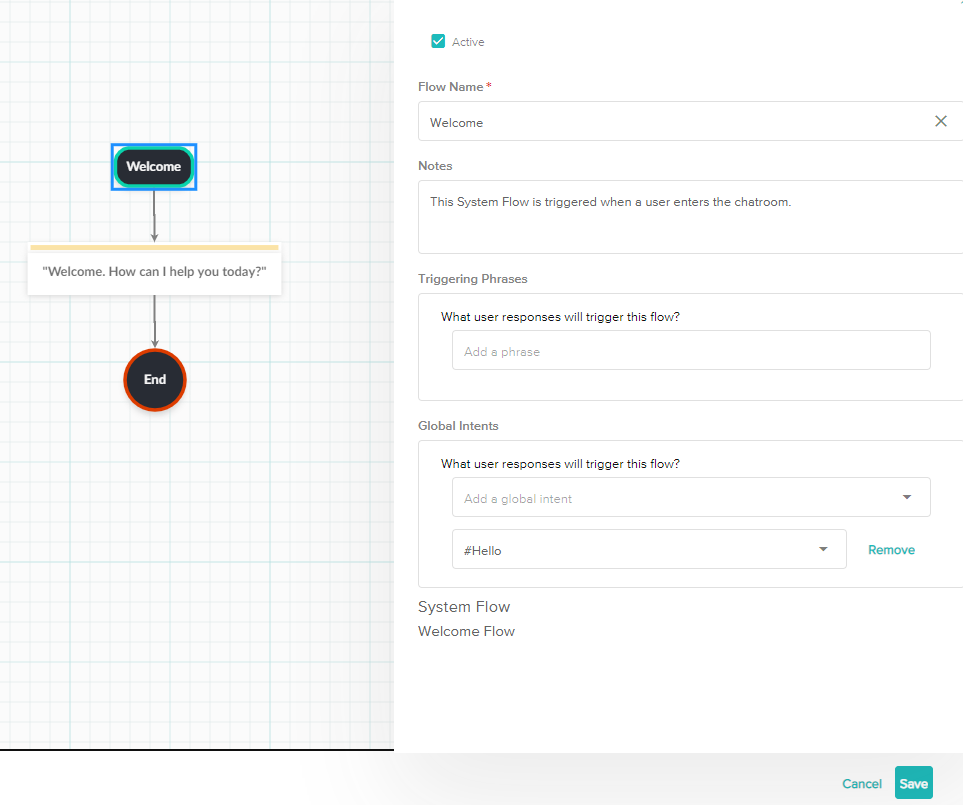
- The Start Node is the Flow's entry point.
- You can only have one Start node.
- Whatever you name this node will be the name of the Flow.
- You can add Triggering Phrases to a Start Node.
- When an End User's message matches one of the triggering phrases, the Flow will be called so long as the End User is not responding to a user response node in a bot message.
- Bot Message Node
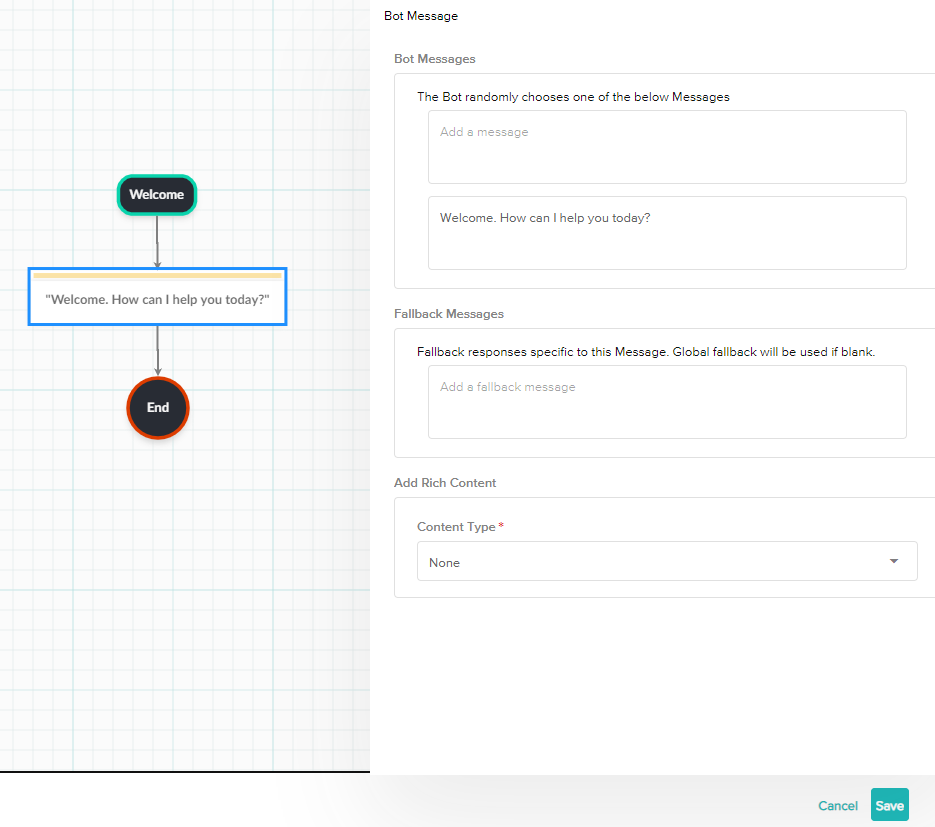
- Bot Messages
- Multiple Bot Messages can be entered in the node as variants.
- The Bot will choose a message at random each time the node is called.
- Fallback Messages
- The local fallback message is triggered when the Bot does not understand the End User's message (ie the End User's input did not match any Q&As, Intents or Entities).
- Rich Content
- Rich Content is either a Knowledge Article, an Image, or a File that the Bot can send to a customer in a Bot Message.
- Bot Messages
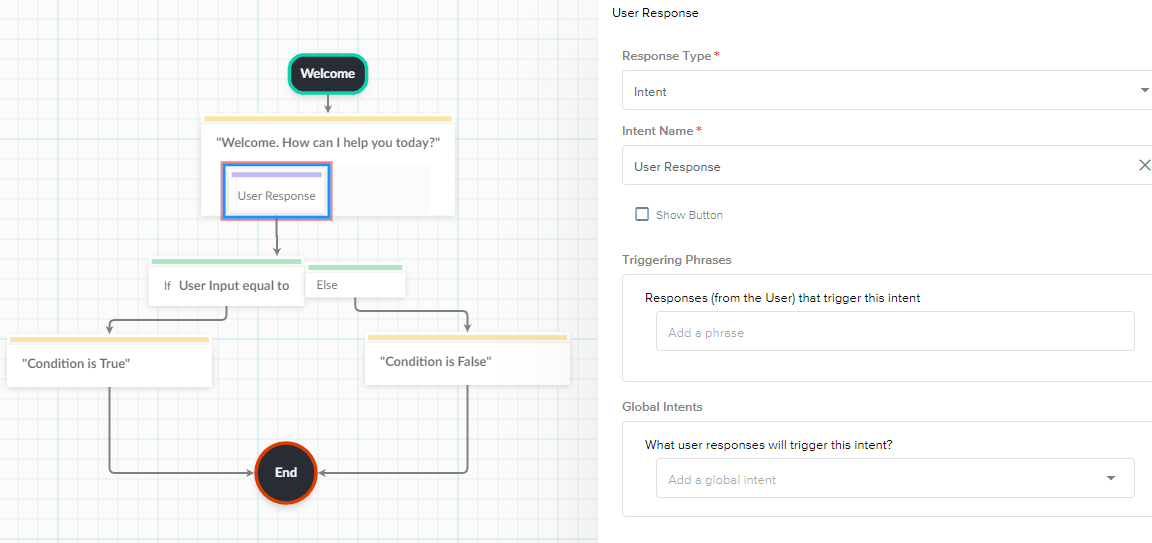
- User Response Node
- Intent
- An Intent refers to the goal the user has in mind when typing in a question or comment.
- Attaching the Intent Node type to a Bot Message Node allows the Builder to define how to handle user inputs.
- Intents are to verbs as Entities are to nouns.
- You can add phrases to the User Response Node or map a Global Intent.
- Entity
- An Entity refers to data objects / user information and is often used synonymously with Custom Fields on the BT Platform.
- Entities are to nouns as Intents are to verbs.
- There are different Entity Types. Categorical, Numerical, Phone Number, Email, Text (Regex).
- Any Response
- Any response will take any message from the End User and accept it as valid input.
- No Response
- The No Response response type allows the bot to determine where to route the flow if the End User does not respond within a specified timeframe.
- Intent
- Branch Node
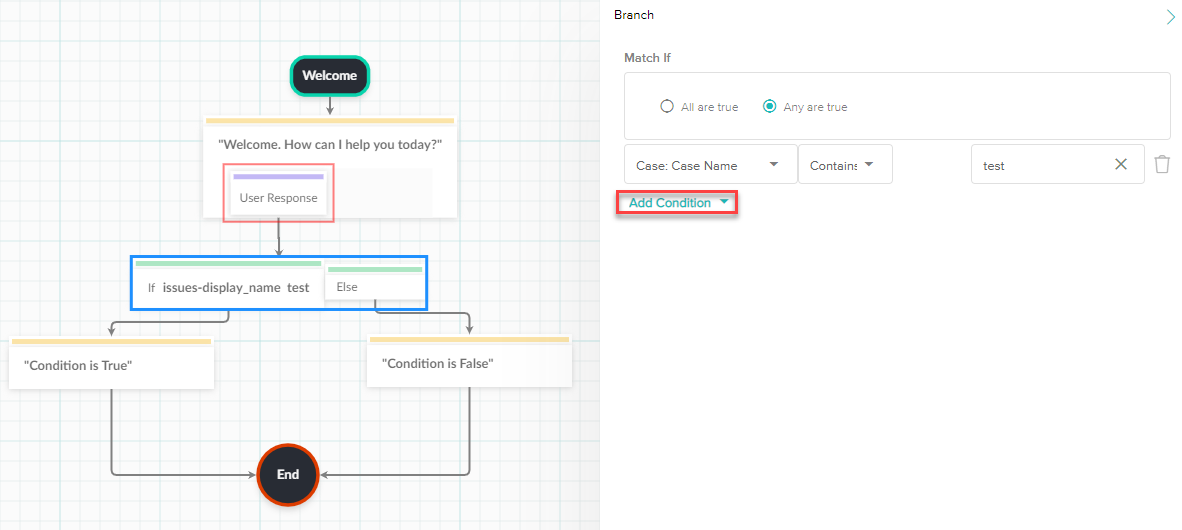
- The Branch allows you to use conditions to determine where the flow will route next.
- There are two directions the flow can route, the If and the Else.
- If
- Determines if the condition set is True. If the condition is True then the flow will route to the node that is connected to the If node.
- Else
- Determines if the condition set is False. If the condition is False then the flow will route to the node that is connected to the Else node.
- If
- Action Node
- Route Conversation
- Routing the conversation will assign the case to a team of your choosing.
- You can also choose whether to route the conversation when the team is available or even when they're unavailable.
- Use this Action Node for Agent Handoffs which ideally should be managed from the Route Conversation prebuilt flow.
- Change Data Value
- You can change specific fields of the case with this option. The previous node connected to this node must be a User Response Node or a Data Capture Node so the Action Node knows what to change the field to.
- Resolve Case
- This will resolve the case.
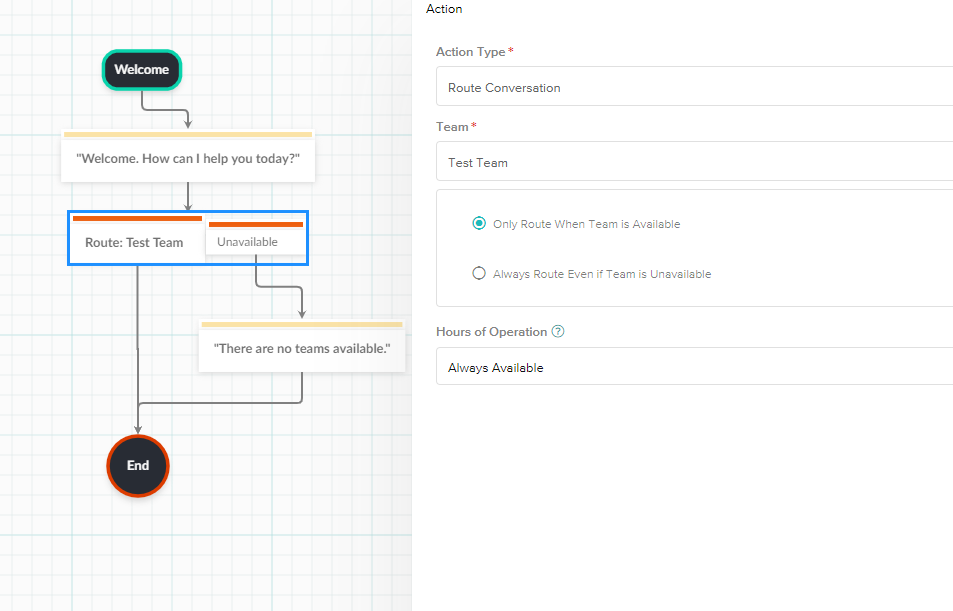
- Route Conversation
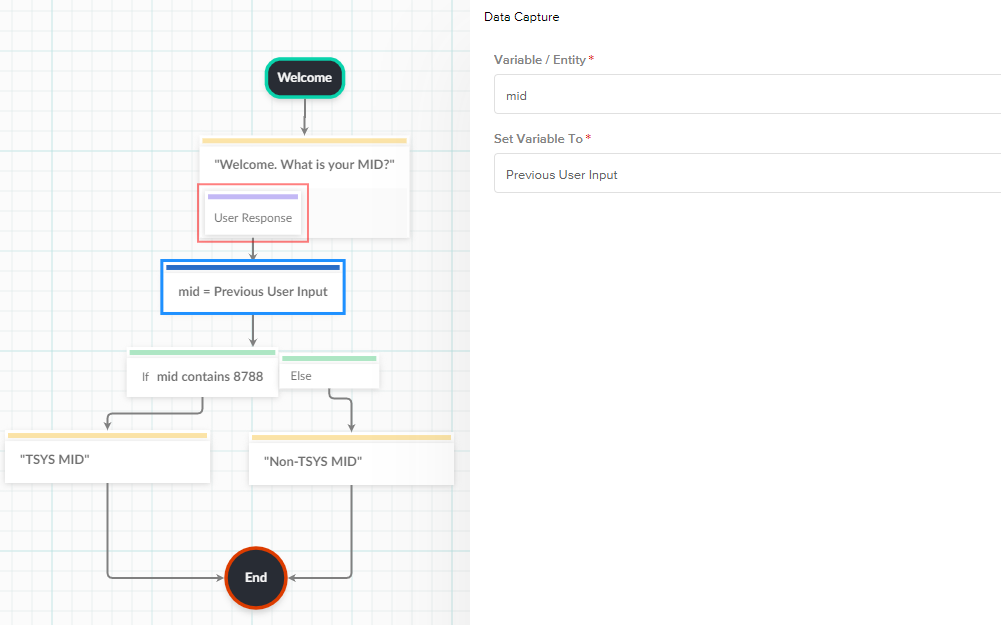
- Data Capture Node
- The Data Capture Node allows you to gather information from a user and assign it to an Entity.
- Variable/Entity
- You can choose an Entity to assign a value to and this Entity can then be used throughout the flow.
- You can set the value to Previous User Input, the name of the Previous Intent, or you can manually set it to anything you want.
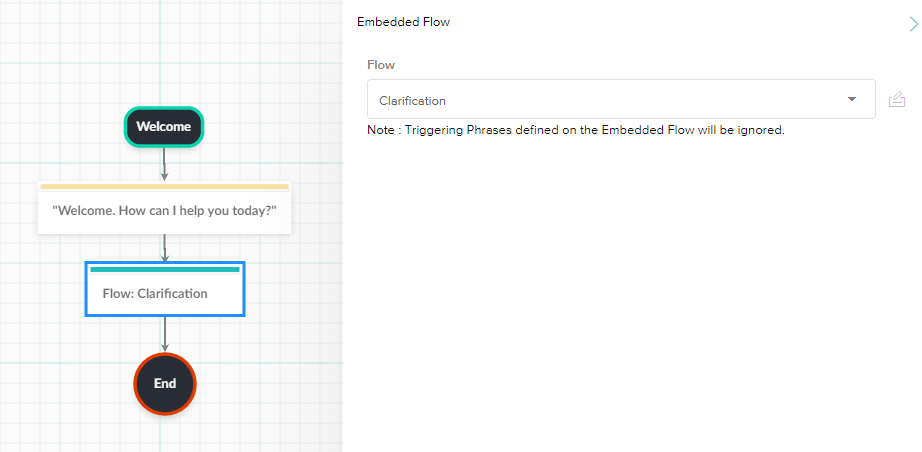
- Embedded Flow Node
- The Embedded Flow Node allows you to route the current flow to another flow.
- Embedded flows are a way to componentize patterns in a conversation that repeat and you only want to manage in one place. If you make updates to that embedded flow it will update everywhere it is embedded.
- Embedded Flows are also referred to as Sub Flows.
- End Node
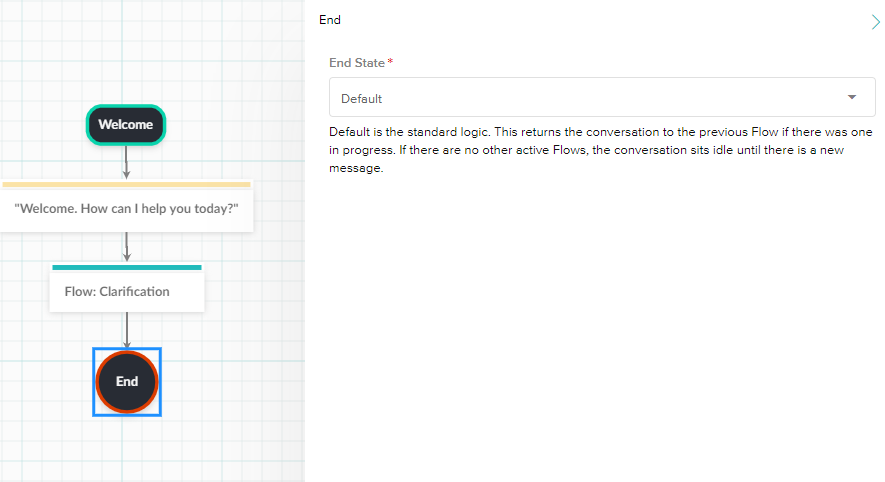
- End State
- The Default End State will route the conversation to the previous flow if there was one in progress. Otherwise, it stays idle until there is a new message.
- The Force Idle End State stops the conversation and ends any Flows that were previously in progress. The bot will remain idle until there is a new message.
- The Halt End State stops the conversation and removes the bot from the chat room permanently. It cannot be added back.
- If the Flow is embedded inside of another flow, the original flow will continue along its path when the embedded flow reaches the end node.
- End State